L519: Lab Session 12 (12/2/05)
Today's Topics
- Rfam : RNA families database of alignments and CMs
- RNA Structure Prediction Programs
- L519 Course Review
¤ Rfam : RNA families database of alignments and CMs
- Rfam Site : http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Software/Rfam/
- Joint project involving researches based at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, and Washington University, St. Louis
- Large collection of multiple sequence alignments (MSA) and covariance models (CM) covering many common non-coding RNA families
- Current version 7.0 with 503 families
- Historically, structure-based RNA sequence analysis has been difficult to automate. Most RNA structural alignments are the product of expert manual curation. Recent software advances using secondary structure profiles called ‘covariance models’ (CMs—also called profile stochastic context-free grammars) have led us to begin the development and automated maintenance of a database of structural RNA alignments. This is analogous to the use of profile hidden Markov models of primary sequence consensus in the development and maintenance of thousands of protein sequence alignments in the Pfam database.
- Sample search : U2, Alignment in FASTA
- Download : www.sanger.ac.uk/Software/Rfam/ftp.shtml
¤ RNA Structure Prediction Programs
- MFOLD
- Most widely used software incorporating minimum free energy
- Developed by Michael Zuker
- The Zuker Group website
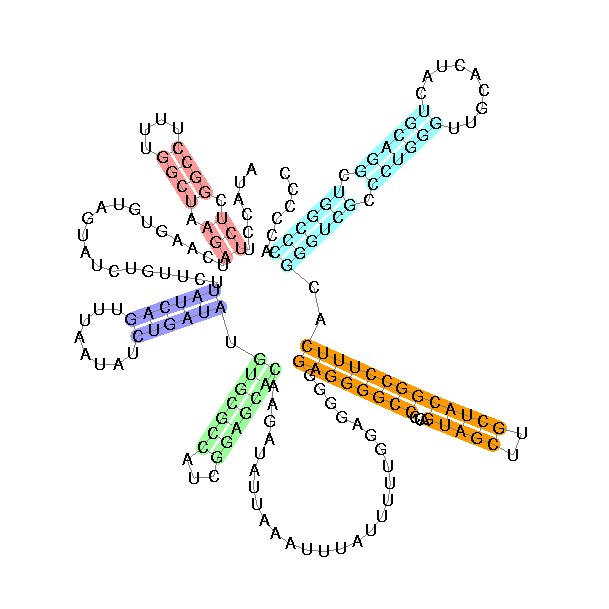
- Sample Sequence (X63784, U2 RNA)
- Online server: http://www.bioinfo.rpi.edu/applications/mfold/old/rna/form1.cgi
#1 #2 #3 #4 #5
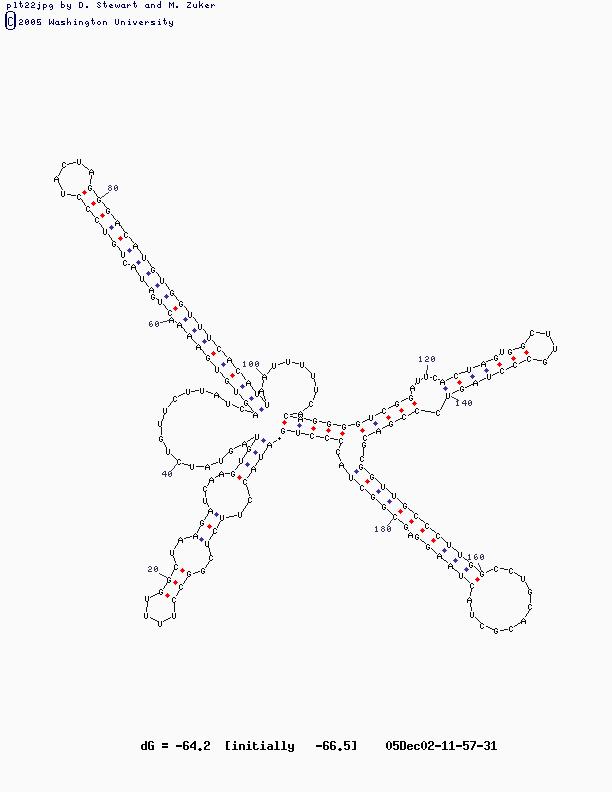
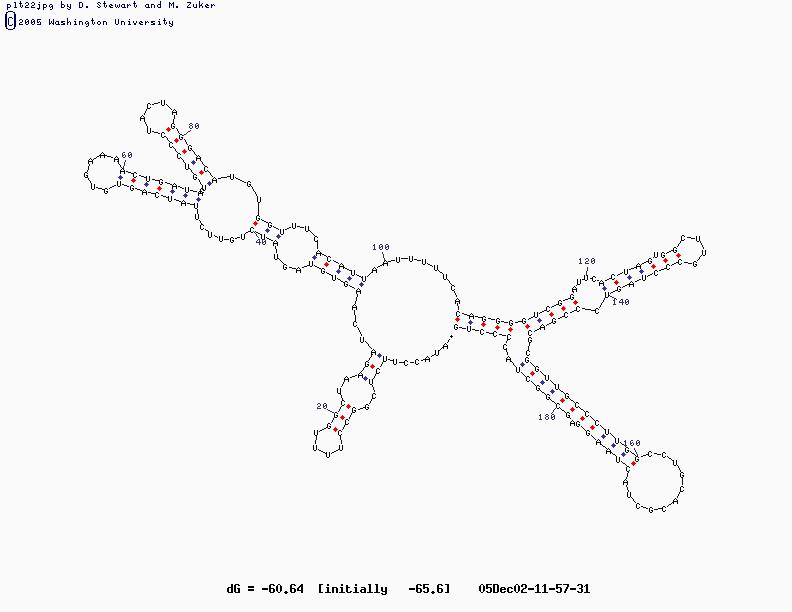
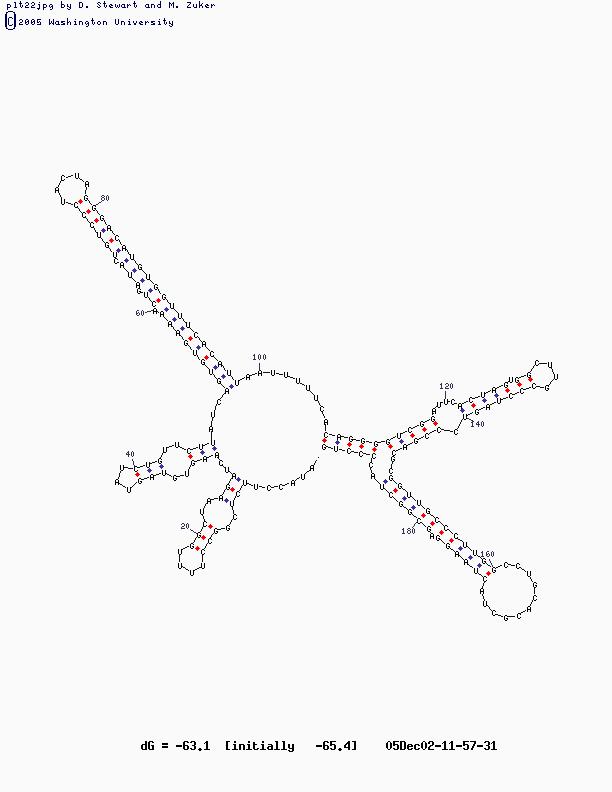
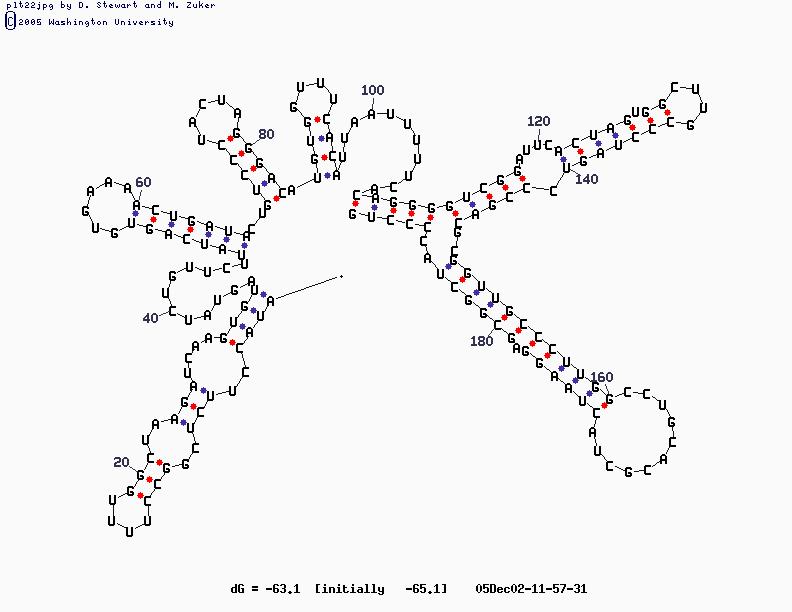
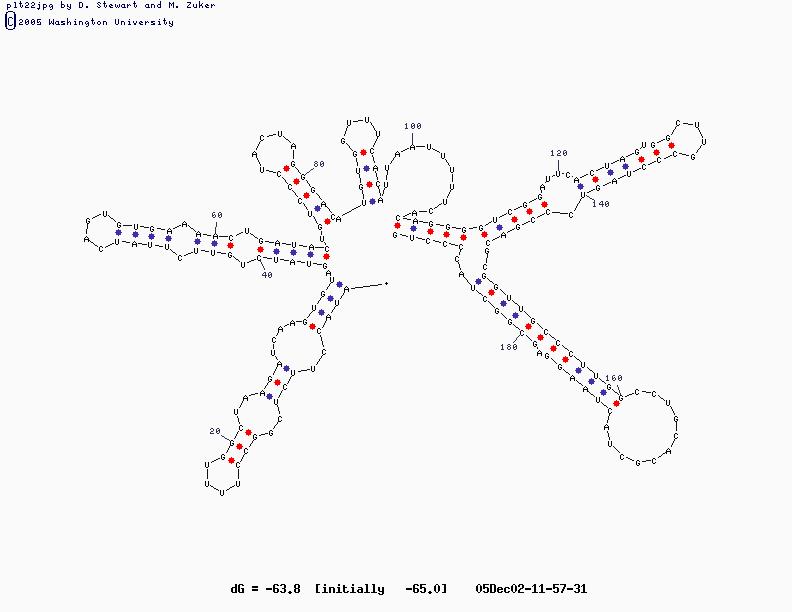
U2 Structure
- Download: http://www.bioinfo.rpi.edu/~zukerm/export/mfold-3.html Manual
- Biokdd: /tmp/L519FALL2005/mfold/bin/
- Env Setting : MFOLDDAT="/tmp/L519FALL2005/mfold/dat"
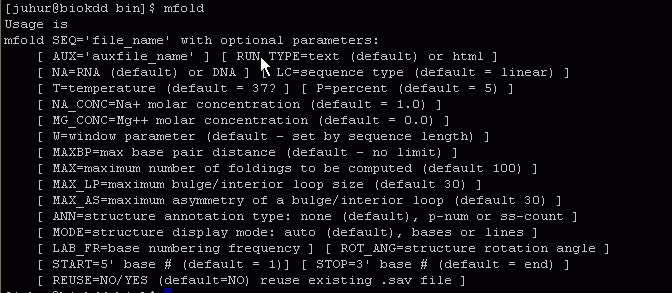
- >mfold SEQ="testSeq.fas" RUN_TYPE=html
- Vienna RNA Package
- RNA secondary structure prediction through energy minimization
- Provides three different dynamic programming algorithms for prediction
- The minimum free energy algorithm of (Zuker & Stiegler 1981) which yields a single optimal structure
- The partition function algorithm of (McCaskill 1990) which calculates base pair probabilities in the thermodynamic ensemble
- The suboptimal folding algorithm of (Wuchty et.al 1999) which generates all suboptimal structures within a given energy range of the optimal energy.
- For secondary structure comparison, the package contains several measures of distance (dissimilarities) using either string alignment or tree-editing (Shapiro & Zhang 1990).
- They also provide an algorithm to design sequences with a predefined structure (inverse folding).
- Available programs
- RNAfold -- predict minimum energy secondary structures and pair probabilities
- RNAeval -- evaluate energy of RNA secondary structures
- RNAheat -- calculate the specific heat (melting curve) of an RNA sequence
- RNAinverse -- inverse fold (design) sequences with predefined structure
- RNAdistance -- compare secondary structures
- RNApdist -- compare base pair probabilities
- RNAsubopt -- complete suboptimal folding RNA secon
- RNAfold webserver
- Source code is available from the homepage.
- Other programs (The RNA World Website)
¤ L519 Course Review